Blockchain EBL – The future Bill of Lading
Blockchain EBL – The future Bill of Lading
Blockchain EBL – The future Bill of Lading
Overview
A bill of lading is one of the most common – and important – documents in the shipping and logistics industry. It’s been a key aspect of international trade for centuries, and because of its pervasiveness in the industry, it’s easy to overlook this type of document. But to do so would open you up to a world of shipping troubles.
What is Bill of Lading?
Typically abbreviated as B/L or BoL, a bill of lading is a legal transport document issued by a carrier to a shipper. It plays three different roles:
Evidence of contract of carriage with details of the amount, type, and destination (and even sometimes the condition) of the shipped freight
Receipt that the goods have been properly loaded onto the transporting vessel
Title of goods, which often requires the carrier to turn over the goods to the consignee (receiving party) noted on the BoL.
Historically, the word “lading” comes from an Old English term meaning “loading.” These bills have existed in some form or another since the Roman times, but they became a more common practice during the Medieval times.
Why is Bill of Lading important ?
BoLs are vital to the successful transportation of goods. Primarily, the document serves as a legally-binding agreement which helps the carrier process the cargo according to the original contract terms set up by the carrier and shipper or freight owner. This means the BoL can be used in litigation concerns, and inaccurate BoLs can expose carriers to anything from claims to criminal prosecution.
Additionally, since most BoLs are considered a title of goods, these documents (much like the cargo they list) can be used in negotiations. Because of this, some types of BoLs can be endorsed and transferred to third parties while the cargo is in transit, ultimately giving control of the cargo to different parties along the route. This also means that if a carrier hasn’t been paid in full for the transportation of the cargo, the carrier can keep the bill of lading and goods until terms of the sale are finalized.

What’s on a Bill of Lading ?
Depending on the type of BoL (see below), various information should be listed on the document, including:
- Carrier name and a signature from the carrier, the ship’s master, or a legal representative of either of these parties.
Date and indication of goods being loaded onto a vessel
Notation of the port of loading and the port of destination
Terms and conditions of carriage or a reference to these conditions listed in another
document
Detailed description of the goods being shipped (value, count, weight, size,
markings/numbers, etc.)
Name of the consignee
Any special instructions for shipping
This information is just some of the items which may be required on a BoL. A marine/ocean shipping BoL, for example, will also need the name of the ship written on the document.
This information is just some of the items which may be required on a BoL. A marine/ocean shipping BoL, for example, will also need the name of the ship written on the document.
What are different types of Bill of Lading?

There are several different kinds of BoLs, but only some of them are used on a regular basis:
01
Straight:
As the name indicates, this BoL is used when goods are already fully paid for and shipped directly to the consignee/customer. Straight BoLs are non-negotiable.
02
Shipper’s:
These BoLs are used when cargo is purchased on credit, and are handled through a bank. Shipper’s order BoLs are negotiable documents and function like a title of goods. A buyer usually needs the original or a copy of the BoL to take possession of cargo at destination.
03
Air waybill:
These BoLs are exclusively issued for goods transported by air, and are non-negotiable.
04
Originals:
Some BoLs are issued in what’s known as “sets of originals,” and are used to help control the cargo when the consignee/buyer hasn’t yet fully paid the manufacturer of the goods. Once the buyer presents the full set of original documents and pays the manufacturer, the goods can be released to the consignee.

05
Inland:
When cargo is only transported on land (such as over rail or roads), an inland BoL is issued.
06
Multimodal/combined transport:
This type of BoL is exactly what it sounds like: a document issued for a shipment which is using more than one mode of transportation (i.e. ocean, air, land, etc.).
07
Through:
A through BoL is similar to a multimodal/combined transport BoL, but it’s more complex in that it accounts for different distribution centers as well as various modes of transportation. Through BoLs require both an ocean and inland BoL to be effective. Despite the existence of through BoLs, multimodals are still more commonly used across the shipping industry.
08
Switch:
This type of BoL is commonly used during foreign-to-foreign shipments, where the shipper requires their suppliers information to be kept private. During this shipment, there will be two sets of bills “switched” to protect the suppliers information from the consignee and vice versa.
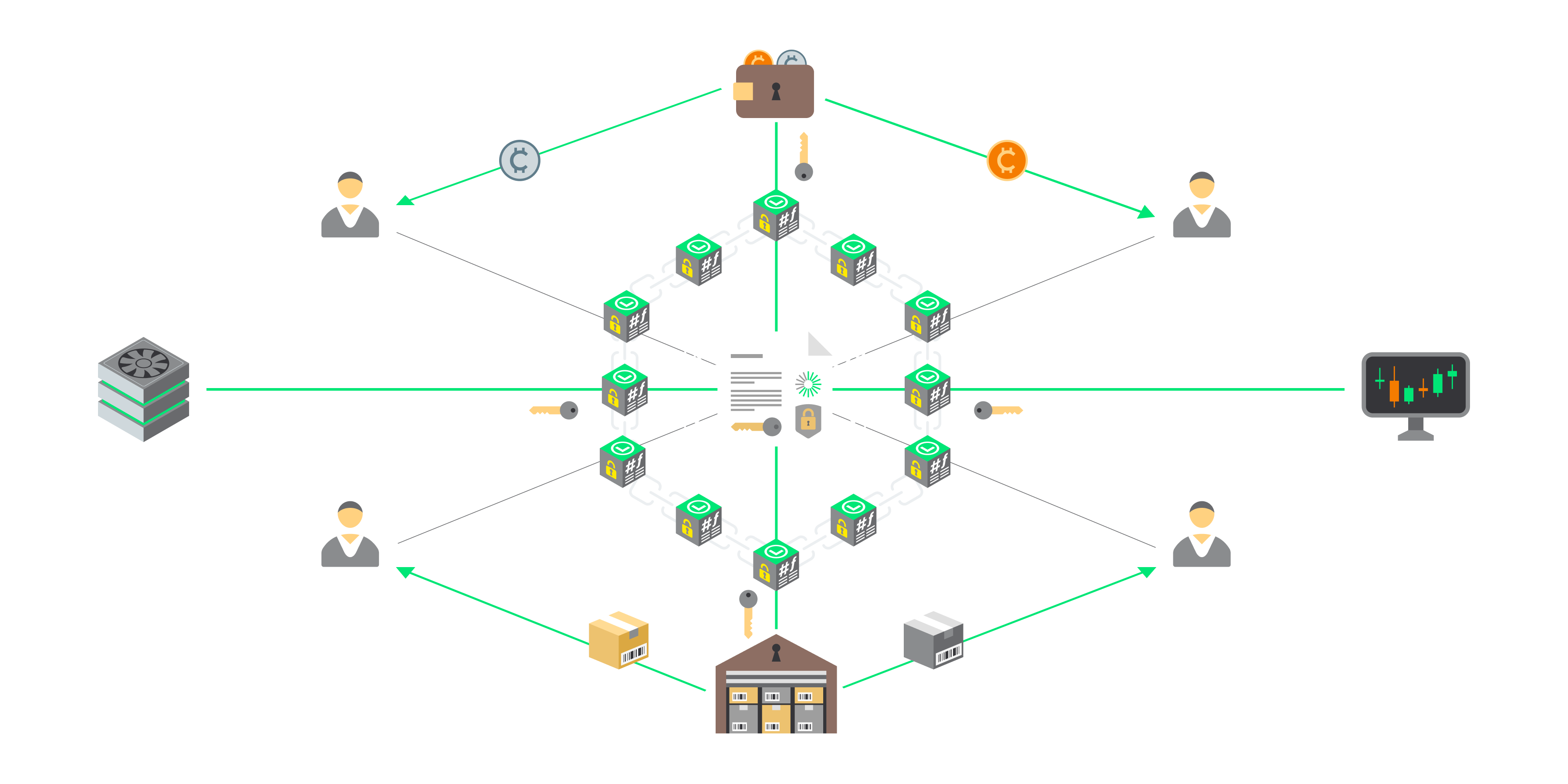
What is EBL?
An electronic bill of lading is a paperless bill of lading that is issued electronically said to fulfil the functions in the same manner as a traditional paper bill of lading. Electronic bills of lading are a digital alternative to traditional paper and courier services that enables instant, authenticated transfer of original electronic bill of lading documents. Some e B/L solutions provide a complete mirror of the paper process with the exception that paper documents are now digital and the transfer is executed via peer-to-peer blockchain technology rather than courier. In other e B/L solutions available on the market the digital transfer is done via a cloud-based system.
Advantages of EBL are as follows :
eB/l is superior to paper/courier in terms of speed, cost and security
eB/Ls protect business continuity
eB/Ls offer greater peace of mind and security
eB/Ls can overcome the problem of short routes
Smart B/L
The blockchain-based Bill of Lading known as Smart B/L preserves all paper B/L legacy features and enhances them with benefits offered by the decentralized ecosystem, including speed, security, and transparency. Additionally, it provides a base for further integration of value-added features such as smart contract Letters of Credit (L/C), insurance, etc.
Technologies Used For Smart B/L

Smart Contract
A smart contract is a distributed computer program residing on the blockchain that will execute itself when special conditions on the blockchain are met. Smart contracts can be seen as a service-providing infrastructure, and every blockchain-based application (distributed application – dApp) has a smart contract at its core. End-users can use existing smart contracts; they do not need to deploy a new smart contract every time they need it (as opposed to the real world, where users would need to sign a new contract between two parties and could not use a public “template”).
Permanent Encrypted Decentralised Data Storage
Storing any large amount of data, such as years’ worth of documents on the blockchain, opens several potential security and scalability issues, and, besides, could become prohibitively
Expensive .IPFS has been identified as the most suitable decentralized storage service for permanent storage. Encryption is mandatory, as all documents and non-public metadata are always encrypted. IPFS offers permanent, reliable, and economic data storage appropriate for e-archiving.
Inter-Planetary File System (IPFS)
The Inter Planetary File System (IPFS) is a protocol designed to create a permanent and decentralized method of storing and sharing files. It is a content-addressable, peer-to-peer hypermedia distribution protocol. Nodes in the IPFS network form a distributed file system. IPFS is an open-source project developed in 2014 by Protocol Labs with help from the open-source community.
Blockchain Token
A blockchain account can provide functions other than making payments, for example in decentralized applications or smart contracts – which is the case for Blockchain Document Transfer (BDT). Blockchain tokens are individual fungible or non-fungible tokens that serve as a digital data transport unit for a transaction from one blockchain account to another. Tokens can serve as cryptocurrency, or as data capsules
Conclusion
Hence we have seen the Bill of Lading is one of the important documents in the Shipping Ecosystem. Further we have seen how we can use Blockchain to make this process more surefire and remove inefficiencies in the process. Further it removes a lot of manual processing and hence removes a lot of human processing errors. Further, it also ensures that there is no question of fraud happening as the documents cannot be altered or cannot be deleted.
AARCHIK is a blockchain development firm with clients in UK, US and Europe. You can get more information on our Blockchain Development Capabilities here :
Have an Inquiry?

Mithun S
Mithun is an avid technology geek at heart and is deeply interested in AI, Metaverse and other emerging technologies. He heads the R&D Practice at AARCHIK Solutions








